
PM Maestro is an AI-powered demonstration agent built using LangGraph.js, Redis and Tavily, designed to automate common Product Management tasks. Redis is used for memory management—including checkpointers, vector databases, and a LLM cache—demonstrating how developers can build robust, AI-driven workflows for real-world scenarios.
Product Managers frequently spend substantial time on repetitive yet essential tasks, such as collecting customer feedback, performing market research, estimating effort, and drafting product requirements. PM Maestro, powered by LangGraph JS, illustrates how these tasks can be effectively automated using AI agents. This repository serves as a practical demonstration of integrating LangGraph with advanced memory management features provided by Redis, including checkpointers, LLM caching, and vector databases, to create reliable, modular AI workflows.
- Language: TypeScript (NodeJS)
- Framework: LangGraph JS (Workflow orchestration)
- Database: Redis (Checkpointer and LLM cache)
- LLM Provider: OpenAI
- Search Tool: Tavily (Web search)
- Slack Bot Integration (Optional): Trigger workflows via Slack
- Salesforce Data Integration (Optional): Enrich context with Salesforce CRM data
- Jira Data Integration (Optional): Enrich context with Jira data
git clone https://github.com/redis-developer/langgraph-pm-maestro.git
cd langgraph-pm-maestronpm installCreate your own configuration by copying the example environment file:
cp .env.example .envSet the following key environment variables:
# OpenAI API
OPENAI_API_KEY=""
OPENAI_MODEL_NAME="gpt-4o-mini"
# Tavily Search API
TAVILY_API_KEY=""
# Redis
REDIS_URL=""npm run devThis command starts the agent locally. Open the LangGraph Studio interface in your browser using the following URL:
https://smith.langchain.com/studio?baseUrl=http://localhost:2024(Testing in Chrome browser is recommended)
PM Maestro supports two primary workflows that demonstrate the capabilities of LangGraph and Redis. These workflows can be adapted easily to various domains or roles:
This workflow performs competitor analysis through web searches and generates a PDF containing a feature comparison matrix of various market players.
This workflow generates a comprehensive Product Requirements Document (PRD) by integrating market research data with information from Jira and Salesforce. The PRD includes MVP scope, effort estimations, technical considerations, and prioritized requirements.
Below is the workflow graph illustrating the market research process:
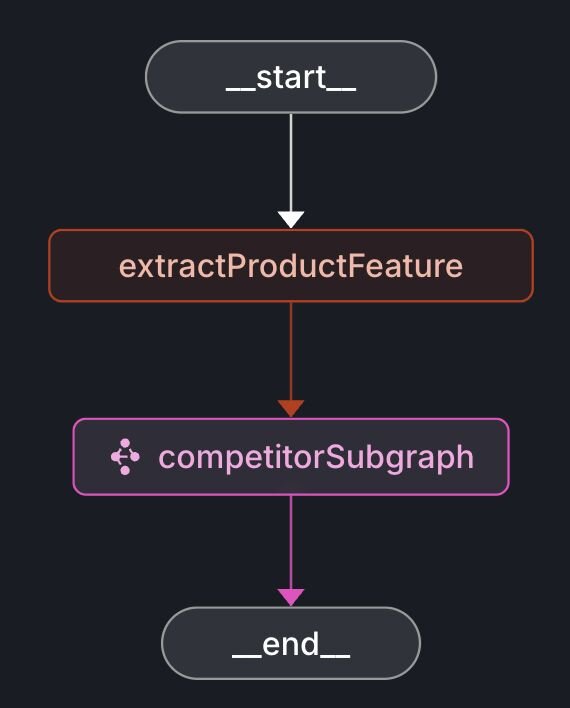
The competitorSubgraph includes additional nodes to retrieve competitor lists and detailed feature information.
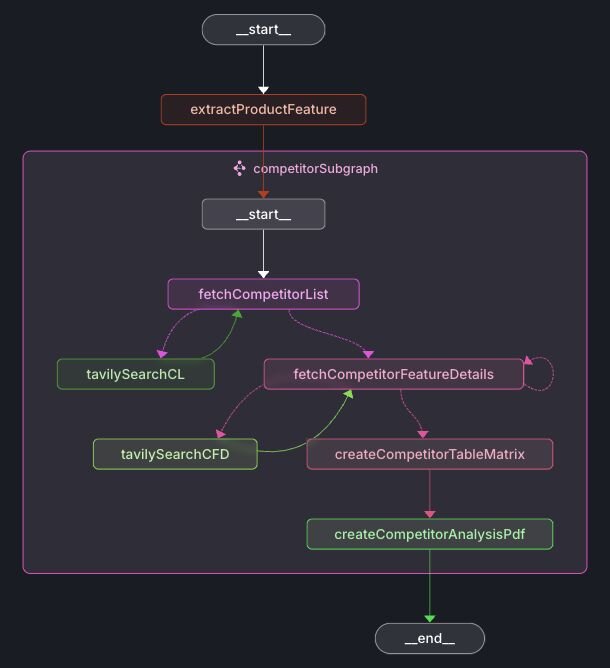
Let's examine each node in the workflow:
- extractProductFeature: Extracts the specific product feature from the user's input.
// Input: "Create PRD for stored procedures feature"
// Output
{
"productFeature": "stored procedures"
}- fetchCompetitorList: Uses the Tavily web search to identify competitors associated with the given product feature.
// Output
{
"competitorList": ["SQL Server", "Oracle", "MySQL", "PostgreSQL"]
}- fetchCompetitorFeatureDetails: Retrieves detailed information about each competitor's implementation of the feature using Tavily.
// Output
{
"competitorFeatureDetailsList": [
{
"competitorName": "SQL Server",
"featureDetails": "Stored procedures in Microsoft SQL Server are a powerful feature that allows users to encapsulate a group of one or more Transact-SQL (T-SQL) statements into a single callable unit..."
},
{
"competitorName": "Oracle",
"featureDetails": "Oracle Database provides a robust stored procedures feature that allows developers to encapsulate business logic within the database. This feature enhances performance, security, and code reuse, making it a powerful tool for building maintainable database applications...."
}
]
}- createCompetitorTableMatrix: Compiles competitors' feature details into a structured comparison table.
- createCompetitorAnalysisPdf: Generates a PDF containing the competitors' feature details and the comparison matrix.
After running the workflow in LangGraph Studio, the generated PDF is saved in the ./prd-files folder as competitor-analysis-<date-time>.pdf.
Note: You can customize the prompts located in the src/agent/prompts/ directory as required.
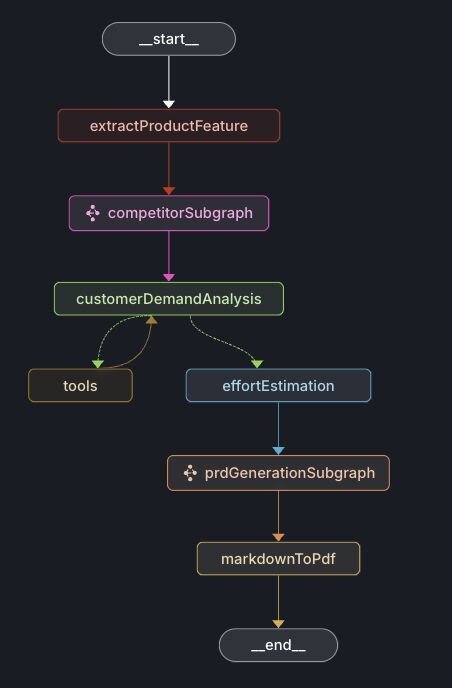
Below is the graph depicting the PRD (Product Requirements Document) generation workflow:
Expanded prdGenerationSubgraph :
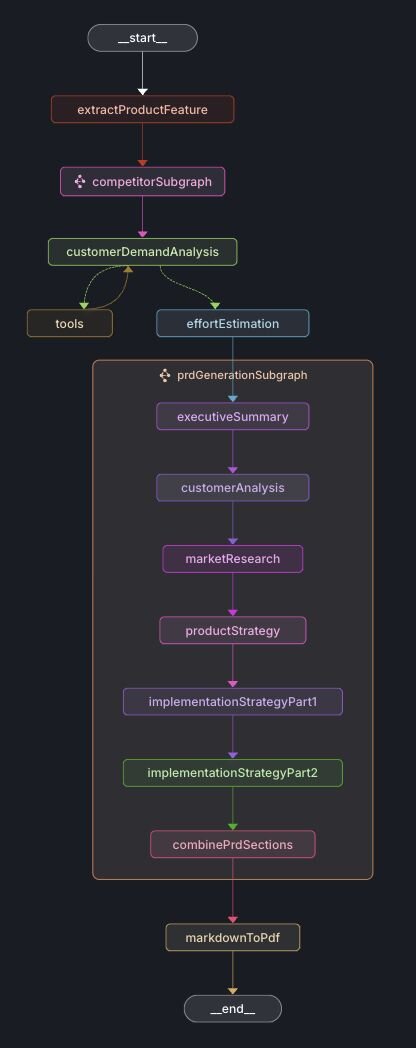
The nodes extractProductFeature and competitorSubgraph are identical to those in the Market Research workflow.
Additional nodes are described below:
- customerDemandAnalysis: Aggregates customer demand data from Jira and Salesforce related to the requested product feature.
- effortEstimation: Estimates the implementation complexity and effort based on competitor analyses and optional customer demand data.
// Output
{
"tshirtSize": {
"size": "M",
"personMonths": 4.5, //over all effort
"rationale": "Medium complexity with existing infrastructure support"
},
"components": [
// sub tasks effort
{
"name": "Backend API",
"description": "Implement REST endpoints for data processing",
"effortMonths": 2,
"customerImpact": "Enables real-time data access for FinTech Solutions",
"technicalComplexity": "Medium"
}
//...
]
}- prdGenerationSubgraph: Creates PRD sections including executive summary, customer analysis, market research, product strategy, and implementation strategy.
- markdownToPdf: Converts the PRD markdown content into a PDF document.
After executing the workflow in LangGraph Studio, the resulting PDF is saved in the ./prd-files directory with the filename mini-prd-<date-time>.pdf.
Note: You can adjust the prompts in the src/agent/prompts/ folder to suit your specific needs.
To integrate Salesforce, sign up at Salesforce Developer to obtain your SF_USERNAME and SF_PASSWORD. You'll also need a SF_SECURITY_TOKEN, which you can get from your Salesforce account by navigating to Settings -> Personal Information -> Reset Security Token.
Configure the following environment variables:
# ==============================================
# SALESFORCE CONFIGURATION
# ==============================================
SF_USERNAME="your Salesforce username"
SF_PASSWORD="your Salesforce password"
SF_SECURITY_TOKEN="your Salesforce security token"
SF_LOGIN_URL="https://login.salesforce.com"
# Example Search Query (SEARCH_FIELD will be dynamically replaced with the requested feature)
SF_SEARCH_FEATURE_QUERY="FIND {SEARCH_FIELD} IN ALL FIELDS RETURNING TechnicalRequest(Id, Name, painPoint, featureRequestDetails, potentialDealSize, industry, priority, currentWorkaround, businessImpact)"Note: Customize SF_SEARCH_FEATURE_QUERY according to your Salesforce organization's structure and objects. Restart the application after updating the environment variables.
To integrate Jira, create an account on Atlassian and set up a Jira Cloud instance. Generate your API token from your Atlassian account's security settings.
Configure the following environment variables:
# signed up profile
JIRA_BASE_URL=https://yourdomain.atlassian.net
JIRA_EMAIL=[email protected]
JIRA_API_TOKEN=your_api_token
# Sample JQL Query - SEARCH_FIELD will be automatically replaced with requested feature
JIRA_JQL_QUERY="project = 'CPG' AND textfields ~ 'SEARCH_FIELD' ORDER BY created DESC"Note: Adjust the JIRA_JQL_QUERY to fit your specific Jira project and data structure. Restart the application after updating the environment variables.
Follow the Slack integration guide to create and configure your Slack app. After setup, configure the following environment variables in your .env file:
SLACK_SIGNING_SECRET="your signing secret"
SLACK_BOT_TOKEN="your bot token"
SLACK_APP_TOKEN="your app token"
SLACK_BOT_PORT=8080Start your Slack bot locally with:
npm run start-slack-bot
# (console output) ⚡️ Slack bot is running and connected!You can trigger the workflows using these Slack slash commands:
- /pm-market-research: Executes the market research workflow.
- /pm-prd: Executes the PRD generation workflow.
In your Slack workspace, test the bot commands with messages like:
/pm-market-research stored procedures feature
# OR
/pm-prd stored procedures featureThe Slack channel displays intermediate messages and final results.
In AI agents, short-term memory refers to the temporary storage of recent information or states that an agent needs immediate access to, enabling it to maintain context and continuity throughout its workflow execution.
LangGraph utilizes a checkpointer to implement short-term memory, allowing the agent to persist intermediate states and recover seamlessly in case of interruptions. In this demonstration, Redis serves as the checkpointer, providing robustness, reliability, and resilience to the agent's workflow execution.
Below is a screenshot illustrating checkpointer data stored in Redis Insight:
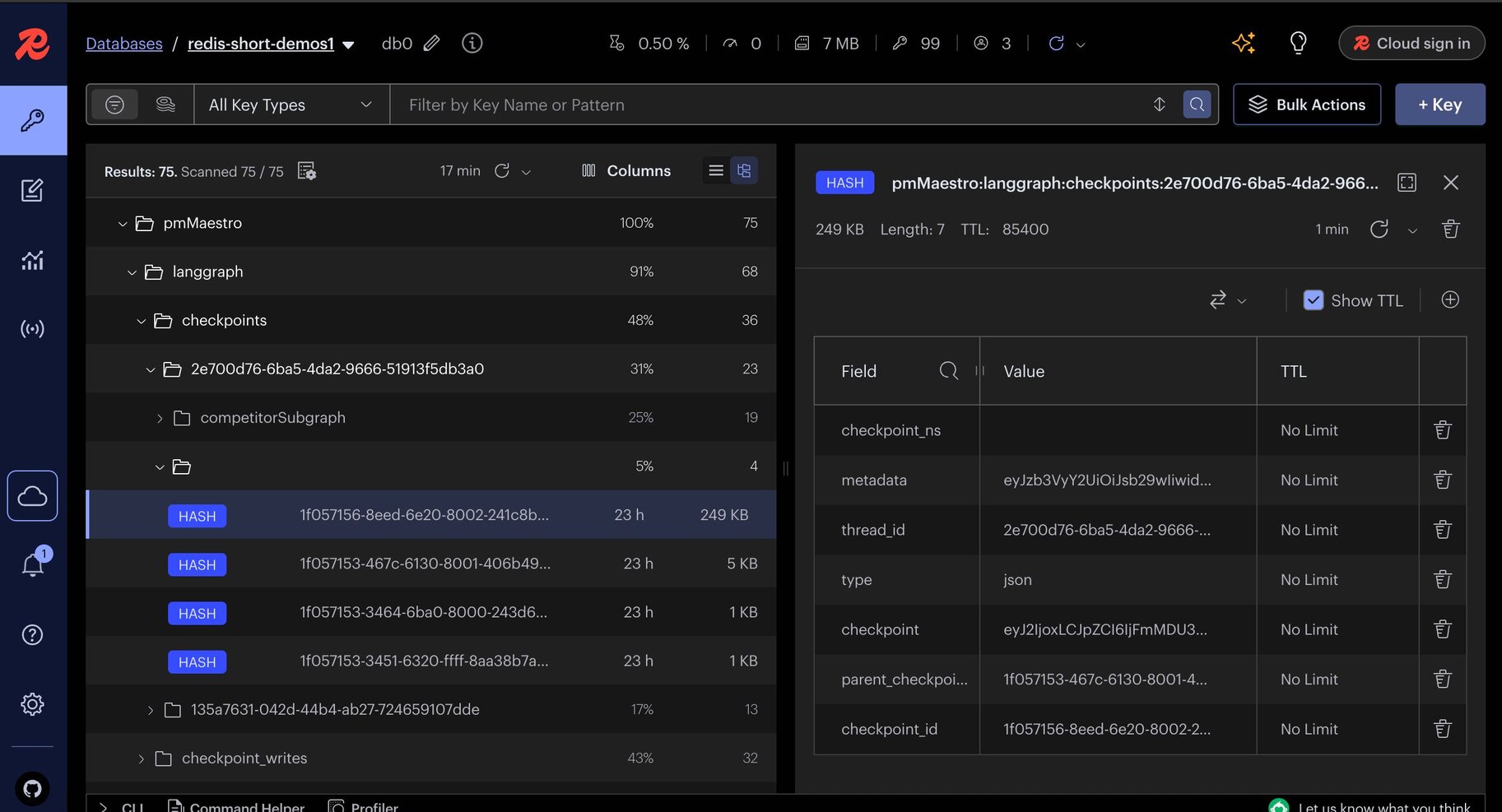
Note: In this demo, a custom Redis checkpointer is implemented, as an official JavaScript integration is not yet available. For the official `Python` Redis checkpointer and store integration with LangGraph, refer to the Python integration repository.
Caching is employed to speed up repeated queries and reduce costs. When you rerun a workflow, cached responses are retrieved directly from Redis, eliminating redundant LLM calls and enhancing overall performance.
- Utilizes vector embeddings (such as OpenAI embeddings) to store and retrieve cache entries based on semantic similarity rather than exact textual matches.
- When a new prompt is processed, its embedding is compared against cached entries. If a sufficiently similar entry exists, based on a configurable similarity threshold, the cached response is returned.
- Enables the retrieval of relevant cached results even when the wording of prompts changes, as long as the underlying meaning remains similar.
- Managed by Redis, Langcache is a service that handles embeddings, similarity search, and metadata within Redis.
- Ideal for scenarios where prompts may differ in phrasing but share the same intent or meaning.
- Stores and retrieves cached entries using exact matches on prompt text along with associated metadata (e.g., feature, node name, user).
- Leverages Redis JSON capabilities for rapid lookups.
- Returns cached responses only if the prompt and metadata match exactly. Semantic similarity is not considered.
- Simpler and faster for identical, repeat queries but less adaptable to natural language variations. Recommended for workflows where agent node inputs remain static or predictable.
| Feature | Semantic Cache (Langcache) | JSON Cache |
|---|---|---|
| Matching | Semantic (vector similarity) | Exact (text and metadata match) |
| Backing Store | Langcache service + Redis | Redis |
| Use Case | Flexible, varied prompts | Identical or static prompts |
| Setup | Requires Langcache service | Redis only |
Below is a screenshot illustrating cache data in Redis Insight:
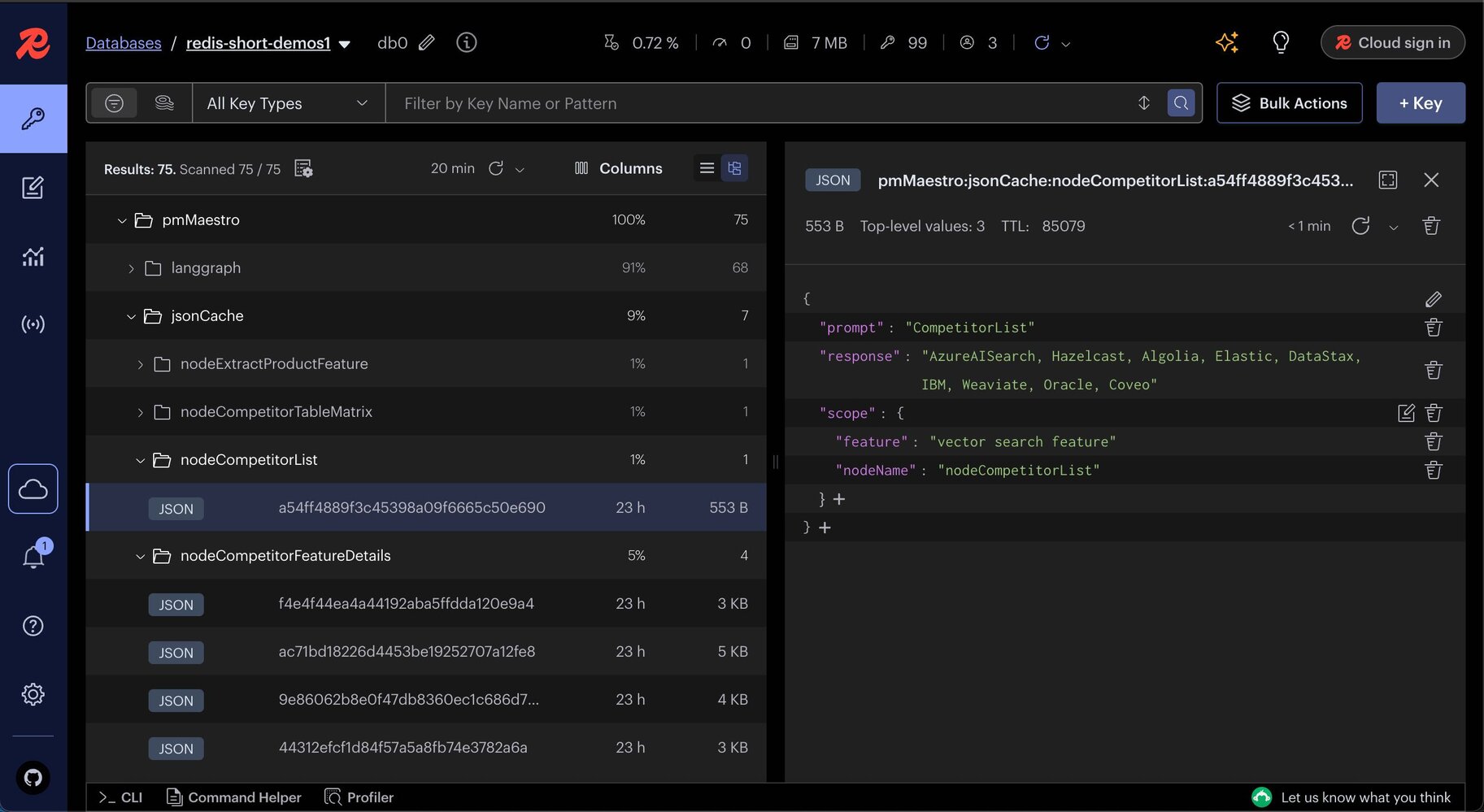
By default, JSON cache is enabled in this demo, since after the product feature is extracted, most subsequent node inputs are predictable keywords and well-suited for exact-match caching. However, you can enable semantic caching (Langcache) by configuring the following environment variables:
LANGCACHE_URL="http://localhost:8080"
LANGCACHE_CACHE_ID="cacheUUID1"
LANGCACHE_ENABLED=""PM Maestro demonstrates the practical capabilities of combining LangGraph JS, Redis, Tavily, and modern AI techniques to create efficient and robust workflows tailored for Product Management. You can further customize and expand these workflows to suit your specific requirements.
- Redis Langgraph checkpointer and store (Python)
- Try Redis Cloud for free
- Redis Insight is a tool to visualize your Redis data or to play with raw Redis commands in the workbench