
What is an Argo CD?
Argo CD is a combination of the two terms “Argo” and “CD,” Argo being an open source container-native workflow engine for Kubernetes. It is a CNCF-hosted project that provides an easy way to combine all three modes of computing—services, workflows, and event-based—all of which are very useful for creating jobs and applications on Kubernetes. It is an engine that makes it easy to specify, schedule, and coordinate the running of complex workflows and applications on Kubernetes. The CD in the name refers to continuous delivery, which is an extension of continuous integration (CI) since it automatically deploys all code changes to a testing and/or production environment after the build stage.
Argo CD follows GitOps methodology. GitOps is a CD methodology centered around using Git as a single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and application code. It watches a remote Git repository for new or updated manifest files and synchronizes those changes with the cluster. By managing manifests in Git and syncing them with the cluster, you get all the advantages of a Git-based workflow (version control, pull-request reviews, transparency in collaboration, etc.) and a one-to-one mapping between what is in the Git repo and what is deployed in the cluster.
Argo CD empowers organizations to declaratively build and run cloud native applications and workflows on Kubernetes using GitOps.
Argo CD is a pull-based, declarative, GitOps continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes with a fully loaded UI. The tool reads your environment configuration from your Git repository and applies it to your Kubernetes namespaces. App definitions, environment, and configurations should be declarative and version-controlled. App deployment and life cycle management should be automated, audible, and easy to understand.
Built specifically to make the continuous deployment process to a Kubernetes cluster simpler and more efficient, Argo CD solves multiple challenges, such as the need to set up and install additional tools outside of Jenkins for a complete CI/CD process to Kubernetes, the need to configure access control to Kubernetes in and out (including cloud platforms), the need to have visibility of deployment status once a new app gets pushed to a Kubernetes cluster, and more.
Argo CD isn’t just deployed inside of Kubernetes but should be looked at as an extension of Kubernetes as it uses existing Kubernetes resources and functionalities like etcd and controllers to store data and monitor real-time updates of application state.
How does Argo CD work?
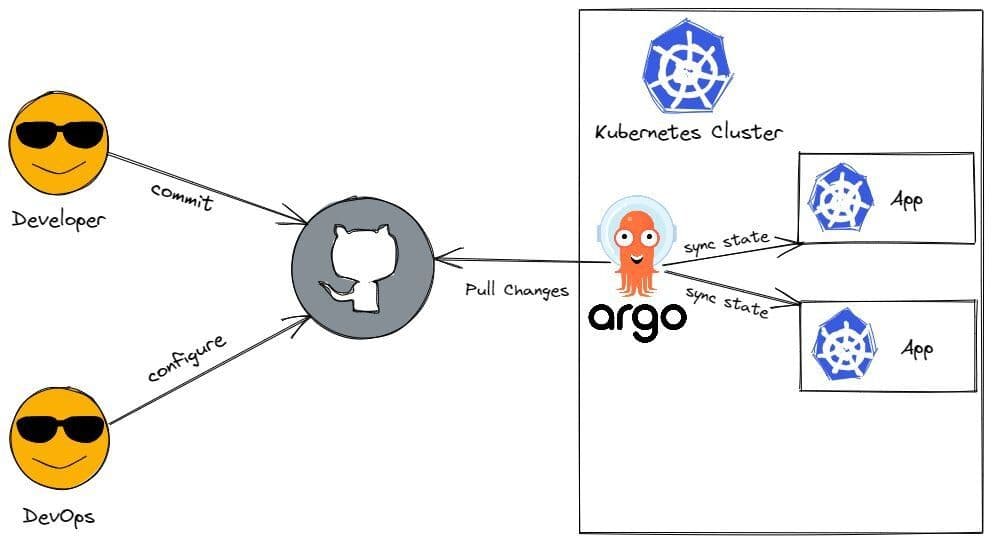
It solves the problems above in the CD process by being a more integral part of the Kubernetes cluster. Instead of pushing changes to the Kubernetes cluster, Argo CD pulls Kubernetes manifest changes and applies them to the cluster. Once you set up Argo CD inside of your Kubernetes cluster, you configure Argo CD to connect and track your Git repo changes.
If any changes are detected, then Argo CD applies those changes automatically to the cluster. Now developers can commit code (for example, Jenkins), which will automatically build a new image, push it to the docker repo, and then finally update the Kubernetes manifest file that will be automatically pulled by Argo CD, ultimately saving manual work, reducing the initial setup configuration, and eliminating security risks. But what about DevOps teams making other changes to the application configuration? Whatever manifest files connected to the Git repo will be tracked and synced by Argo CD and pulled into the Kubernetes cluster, providing a single flexible deployment tool for developers and DevOps.
Argo CD watches the changes in the cluster as well, which becomes important if someone updates the cluster manually. Argo CD will detect the divergence of states between the cluster and Git repo. Argo CD compares desired configuration in the Git repo with the actual state in the Kubernetes cluster and syncs what is defined in the Git repo to the cluster, overriding whatever update was done manually—guaranteeing that the Git repo remains the single source of truth. But, of course, Argo CD is flexible enough to be configured to not automatically override manual updates if a quick update needs to happen directly to the cluster and an alert be sent instead.
What are Argo CD’s capabilities?
Argo CD is a very simple and efficient way to have declarative and version-controlled application deployments with its automatic monitoring and pulling of manifest changes in the Git repo, but it also has easy rollback and reverts to the previous state, not manually reverting every update in the cluster.
It also provides automation and traceability via GitOps workflow with a web UI for visualizing Kubernetes resources.
Argo CD defines Kubernetes manifests in different ways: it supports Kubernetes YAML files, Helm Charts, Kustomize, and other template files that generate Kubernetes manifests.
Argo CD also has a command-line interface application, a Grafana metrics dashboard, and audit trails for application events and API calls.
Argo CD has a very simple cluster disaster recovery process whereby pointing a new cluster to the Git repo if a cluster has gone down will automatically recreate the same exact state without any intervention because of its declarative nature.
Kubernetes cluster access control with Git and Argo CD is simple—you can configure who can commit merge requests and who can actually approve those merge requests, providing a clean way to manage cluster access indirectly via Git. There is also no need to give external access to other tools like Jenkins, keeping cluster credentials safe because Argo CD is already running in the cluster and is the only tool that actually applies changes.
Prerequisites:
-
Install Docker Desktop
-
Enable Kubernetes
-
Install Argo CD
Getting Started
Step 1. Install Argo CD
Step 2. Create a new namespace
Create a namespace argocd where all Argo CD resources will be installed.
Step 3. Install Argo CD resources
Step 4. Ensure that all Pods are up and running
Step 5. Configure Port Forwarding for Dashboard Access

Step 6. Log in
Step 7. Install Argo CD CLI on Mac using Homebrew
Step 8. Access the Argo CD API Server
By default, the Argo CD API server is not exposed with an external IP. To access the API server, choose one of the following techniques to expose the Argo CD API server:
Step 9. Log in to Argo CD
Step 10. Update the password
Step 11. Register a Cluster to Deploy Apps to
As we are running it on Docker Desktop, we will add it accordingly.
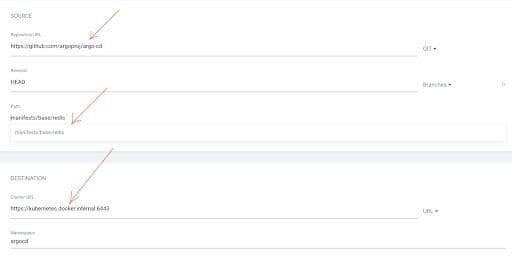
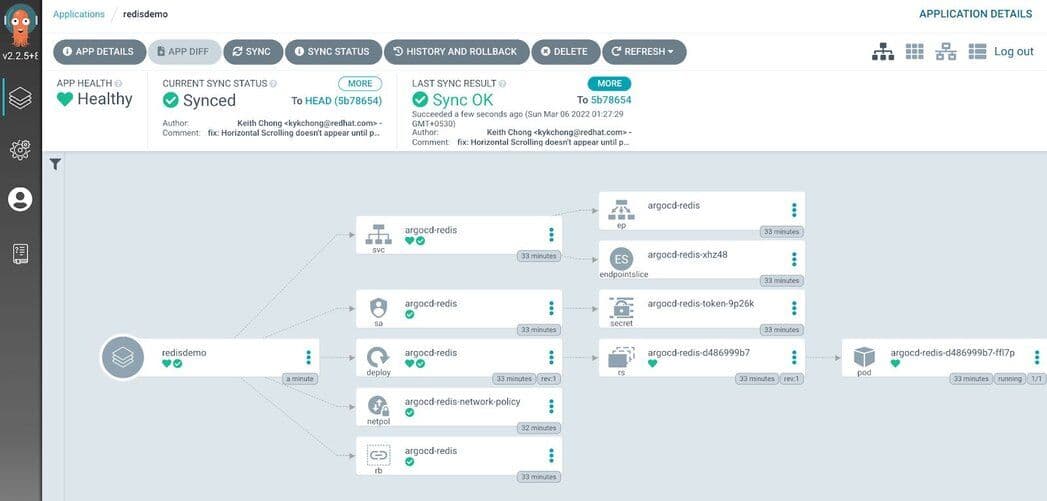
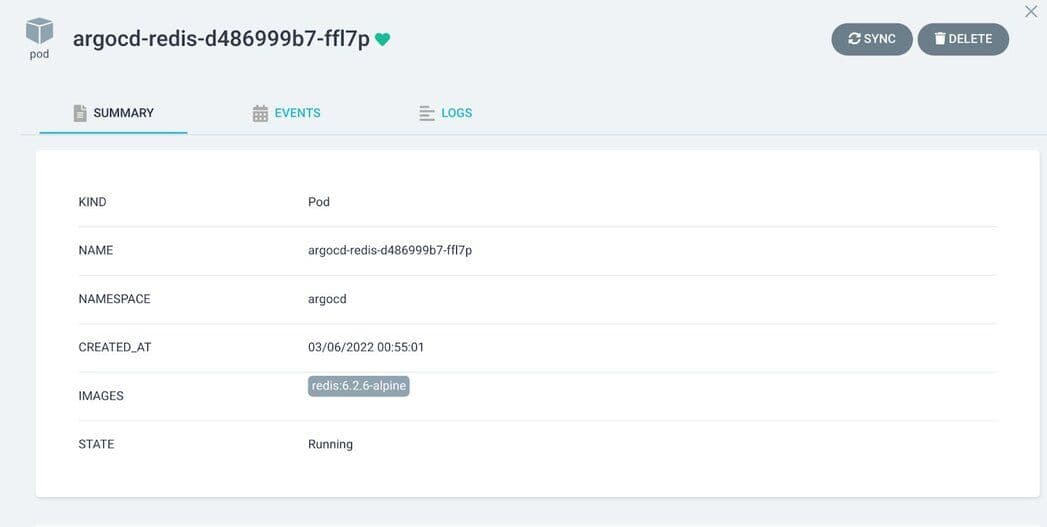
Step 12. Create a New Redis application
Click “Create” and provide a repository URL as https://github.com/argoproj/argo-cd/tree/master/manifests/base/redis

Step 13. Delete the Redis app
Example: Voting App
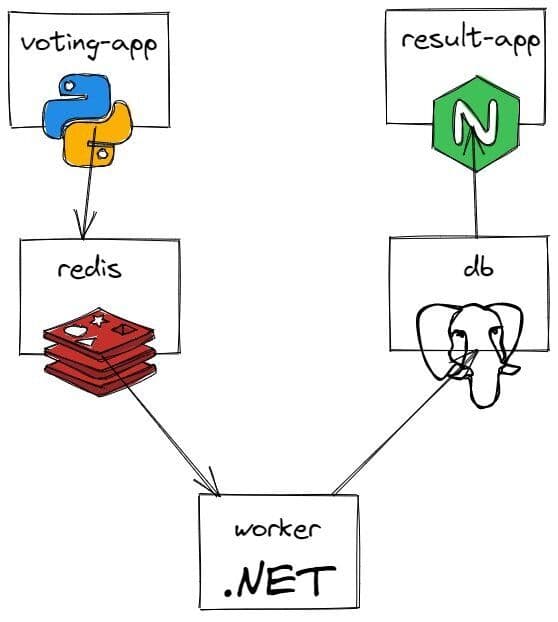
Let’s try to deploy a voting app. The voting application only accepts one vote per client. It does not register votes if a vote has already been submitted from a client.
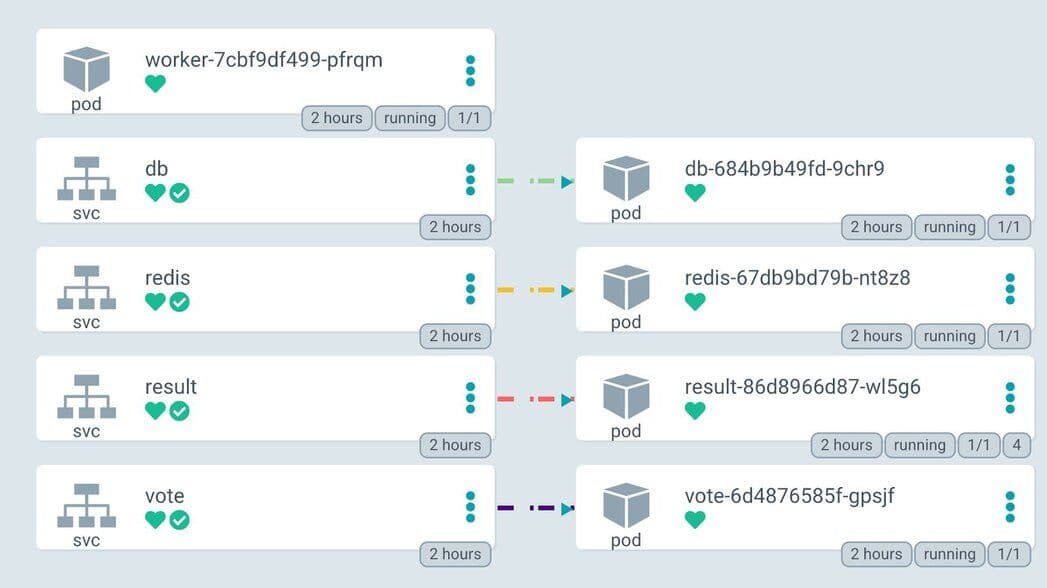
-
A Python web app which lets you vote between two options
-
A Redis queue that collects new votes
-
A .NET worker which consumes votes and stores them in …
-
A Postgres database backed by a Docker volume
-
A Node.js web app that shows the results of the voting in real time
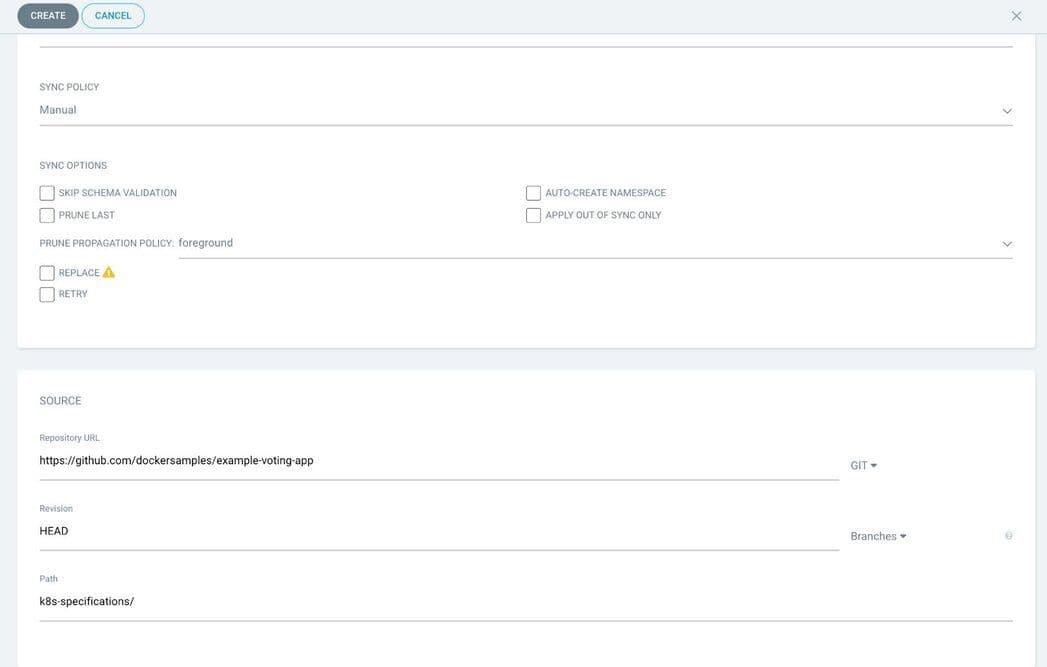
Go to the Argo CD dashboard, enter the repository URL, and supply the right PATH. Click “Create App” to deploy the application on your Docker Desktop.
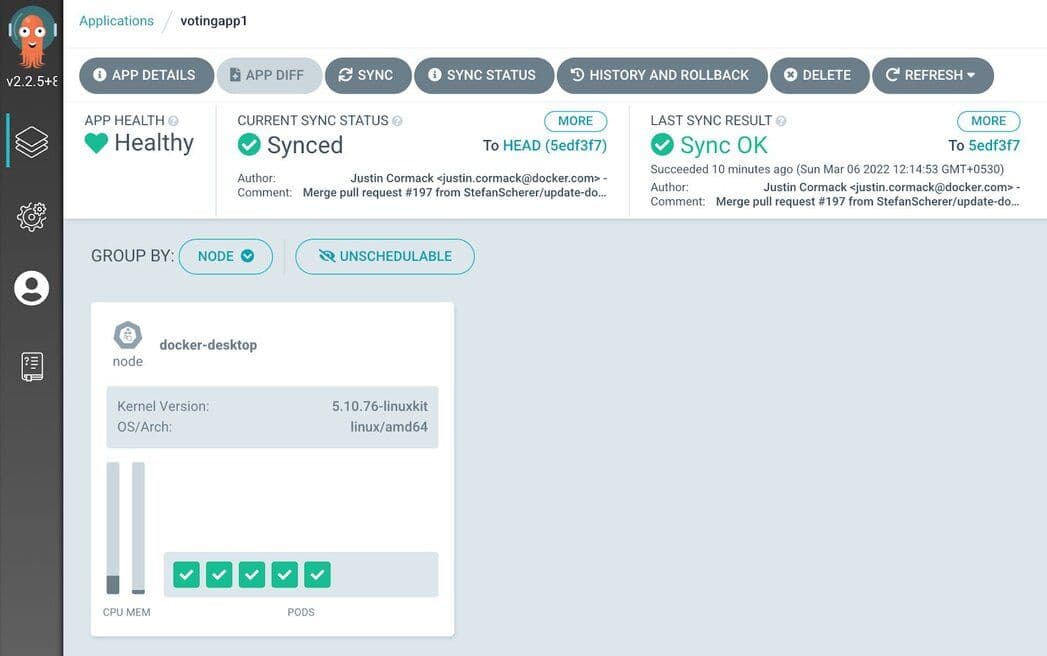
Next, visualize the complete application by choosing “Group by Node.”
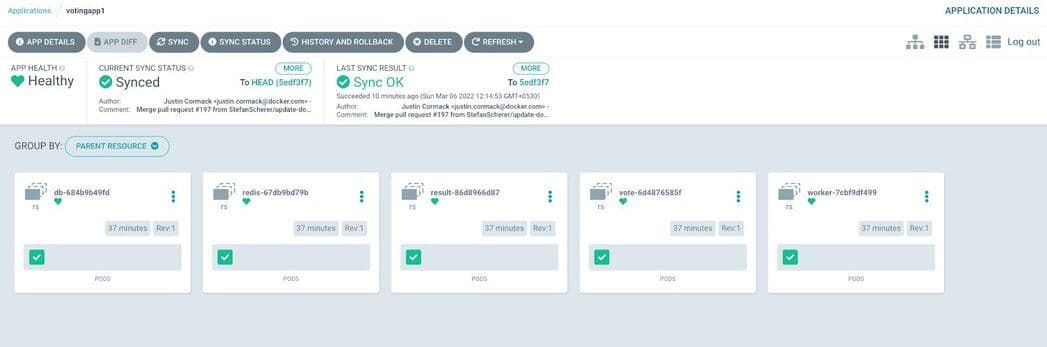
Grouping by Parent Resources
Keep a close watch over the events by clicking on “Events” section.
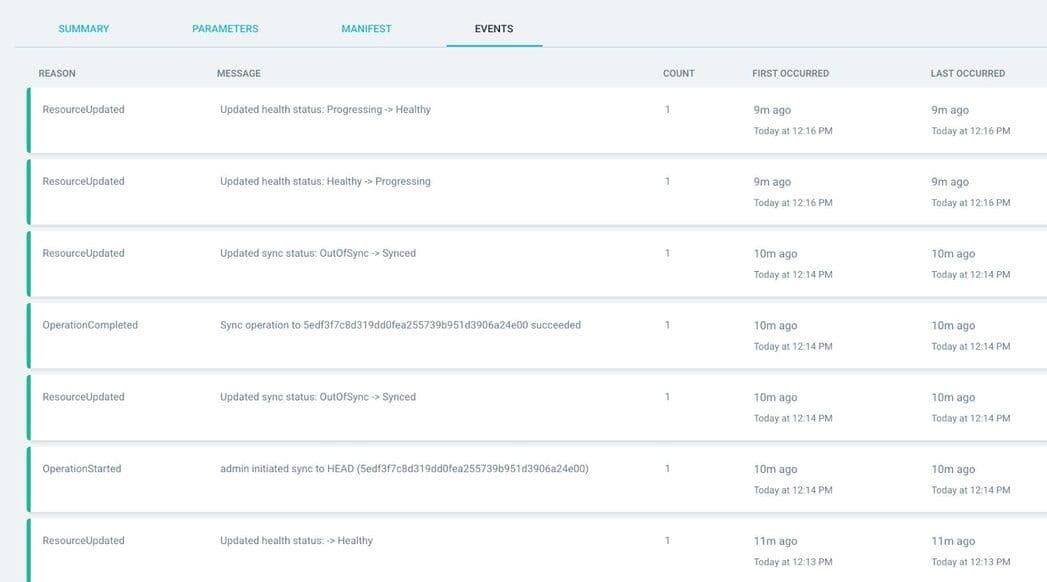
Below is the complete overview of the voting application.
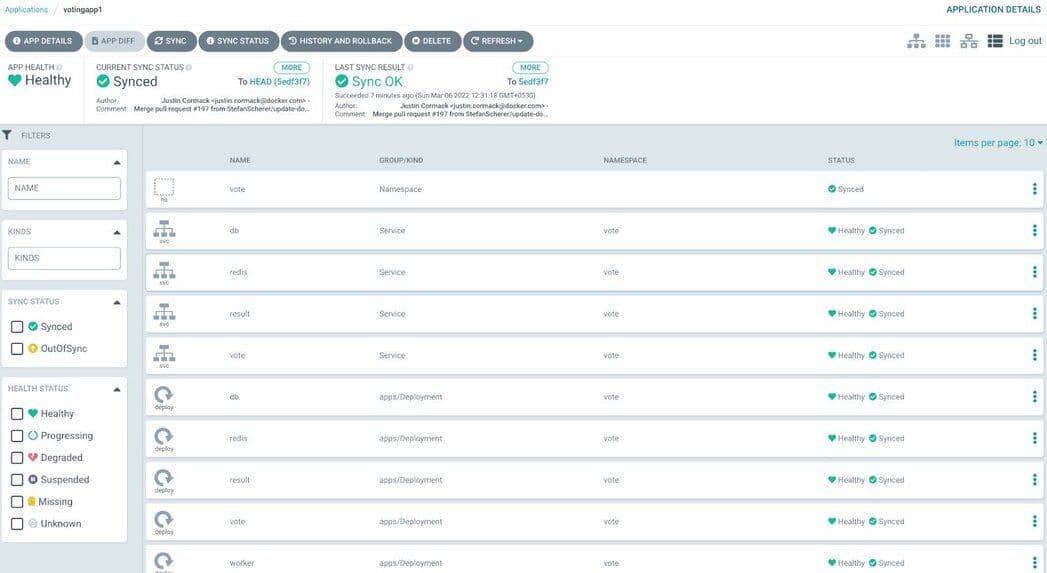
Access the app via http://localhost:31000/
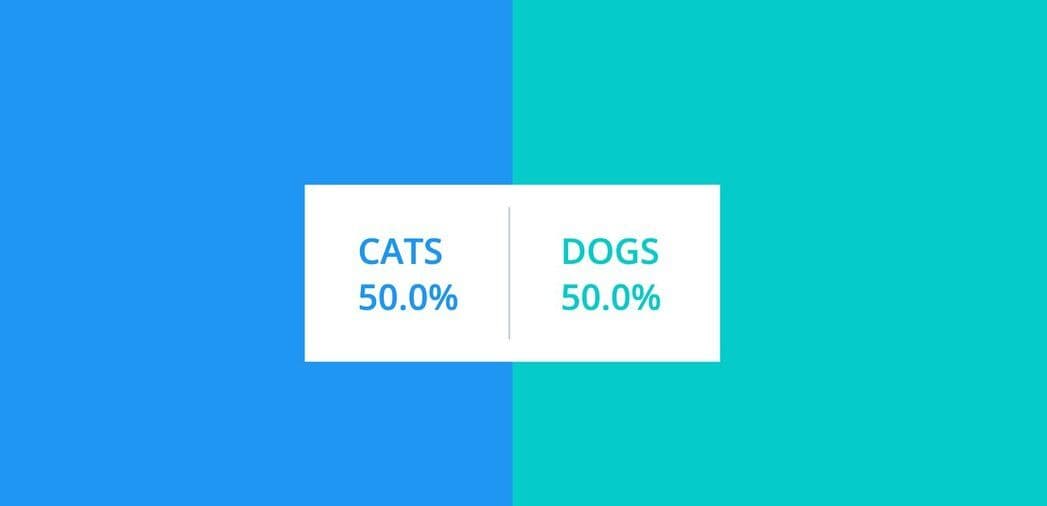
The results are accessible via http://localhost:31001/
Enter some text...